
We need to understand the differences between a backup and an archive, and utilize them effectively in order to cope with issues including regulatory compliance, and data usage within a limited budget.
Backup to prepare
for the event of data loss and damage in an emergency
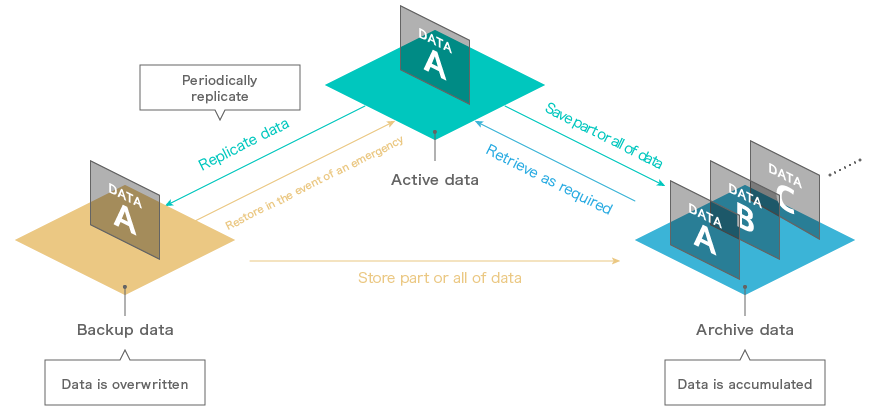
Data backup is the process to periodically copy active data or store only changed/increased data in a tape system.
There is the DtoT (Disk to Tape) method, which backs up active data to a tape system, and the DtoDtoT (Disk to Disk to Tape) method, which backs up active data to a hard disk and then backs up the data on the hard disk to a tape system.
The tape storage is used to save active data temporarily so that it can be restored from the backup data in the event of emergency.
Archive to store
a huge amount of data securely for
a long time
Archiving is a process to store data requiring permanent/long-term storage or cold data selectively from backup data and active data, considering the possibilities of regulatory compliance, corporate governance, and big data business.
Data is restored from an archive and used when required. Thanks to its high reliability and expandability, tape storage has been used as an archive system until now. Along with the increased capacity and transfer rate of tape storage, the range of its use for archive storage is expanding.
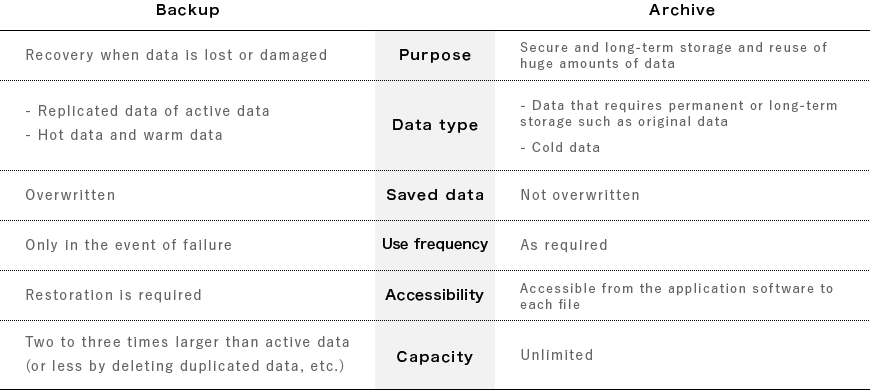
Comparison between Backup and Archive
Storage That Utilizes the Characteristics
of the Magnetic Tape System
Though many of you may have the impression that magnetic tape storage is an old system for backup purposes, the range of magnetic tape system application is expanding from backup to archive purposes thanks to its capability for long-term storage, overwhelming cost performance in large-capacity storage, and also increased transfer rate in recent years, and open-source file management software.
